The Indian Air Force is the air arm of the Indian armed forces. It is the world's fourth largest air force in terms of both personnel and aircraft. Its primary responsibility is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during a conflict. It was officially established on 8 October 1932 as an auxiliary air force of the British Empire and the prefix Royal was added in 1945 in recognition of its services during World War II. After India became independent from the United Kingdom in 1947, the Royal Indian Air Force served the Dominion of India, with the prefix being dropped when India became a republic in 1950. Since independence, the IAF has been involved in four wars with neighbouring Pakistan and one with the People's Republic of China.

The Official Roundel of Indian Air Force
The President of India serves as Supreme Commander of the IAF. The Chief of Air Staff, an air chief marshal, is a four-star officer and commands the Air Force. There is never more than one serving ACM at any given time in the IAF. The rank of Marshal of the Air Force has been conferred once, to Arjan Singh, by the President of India on 26 January 2002 and he became the first five-star rank holding officer of IAF & serves as the ceremonial chief.

Arjan Singh
As said earlier, The Indian Air Force was established in British India as an auxiliary air force of the Royal Air Force with the enactment of the Indian Air Force Act 1932 on 8 October that year and adopted the Royal Air Force uniforms, badges, brevets and insignia. On 1 April 1933, the IAF commissioned its first squadron, No.1 Squadron, with four Westland Wapiti biplanes and five Indian pilots. The Indian pilots were led by RAF Commanding officer Flight Lieutenant (later Air Vice Marshal) Cecil Bouchier.

Westland Wapiti- One of the first palnes of Indian Air Force
During World War II, the IAF played an instrumental role in blocking the advance of the Japanese army in Burma, where its first air strike was on the Japanese military base in Arakan. It also carried out strike missions against the Japanese airbases at Mae Hong Son, Chiang Mai and Chiang Rai in northern Thailand.The IAF was mainly involved in Strike, Close Air Support, Aerial reconnaissance, Bomber Escort and Pathfinding missions for RAF and USAAF Heavy bombers. RAF Pilots were embedded in IAF units and vice versa to gain combat experience. IAF pilots participated in air operations in Europe as part of the RAF.During the war, the IAF went through a phase of steady expansion.




















Hawker Siddley HS 748

HAL HP-32 Deepak

HAL HJT-36 Sitara

HAL HJT-16 Kiran

Pipistrel Virus SW 80

BAE Hawk MK-32

HAL Dhruv

HAL Chetak

IAF Sarang

HAL Cheetah

MIL MI-8

MIL MI-17

MIL MI-26

IAI Searcher II
+Armed+Assault++Attack+Helicopter+(3).jpg)
MIL MI-35

IAI Heron

IAI Harop

DRDO Lakshya (Pilotless Trained Aircraft)
Missiles-

TRISHUL

SPYDER Missile System

S-125 Pechora
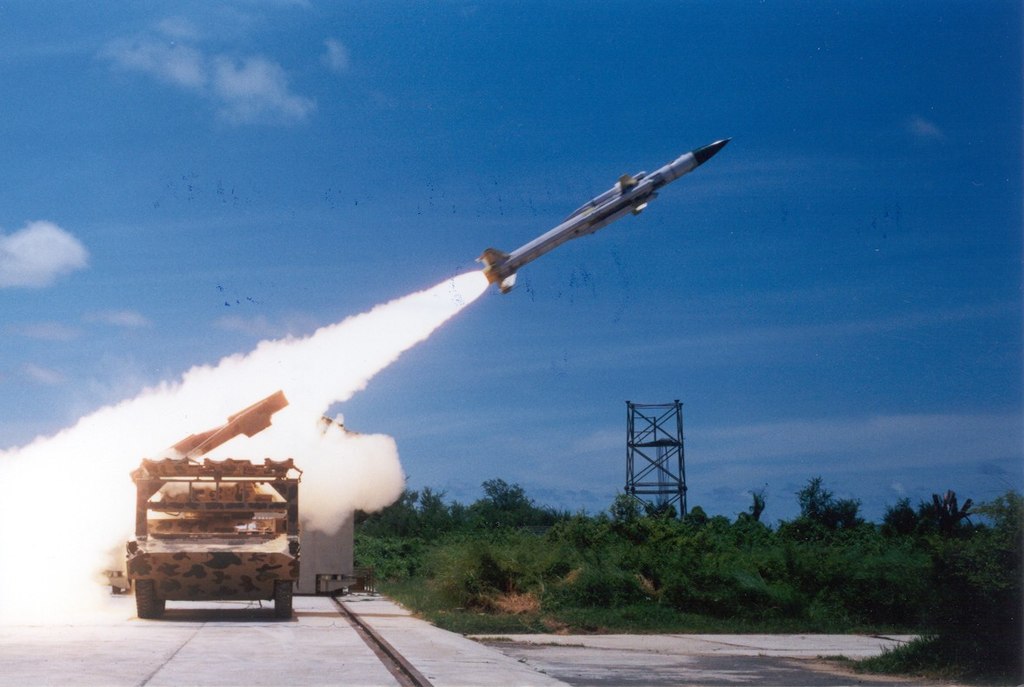

Akash Missile

9K33 OSA

Prithvi-II

Prithvi-I
The Official Roundel of Indian Air Force
The President of India serves as Supreme Commander of the IAF. The Chief of Air Staff, an air chief marshal, is a four-star officer and commands the Air Force. There is never more than one serving ACM at any given time in the IAF. The rank of Marshal of the Air Force has been conferred once, to Arjan Singh, by the President of India on 26 January 2002 and he became the first five-star rank holding officer of IAF & serves as the ceremonial chief.
Arjan Singh
As said earlier, The Indian Air Force was established in British India as an auxiliary air force of the Royal Air Force with the enactment of the Indian Air Force Act 1932 on 8 October that year and adopted the Royal Air Force uniforms, badges, brevets and insignia. On 1 April 1933, the IAF commissioned its first squadron, No.1 Squadron, with four Westland Wapiti biplanes and five Indian pilots. The Indian pilots were led by RAF Commanding officer Flight Lieutenant (later Air Vice Marshal) Cecil Bouchier.

Westland Wapiti- One of the first palnes of Indian Air Force
During World War II, the IAF played an instrumental role in blocking the advance of the Japanese army in Burma, where its first air strike was on the Japanese military base in Arakan. It also carried out strike missions against the Japanese airbases at Mae Hong Son, Chiang Mai and Chiang Rai in northern Thailand.The IAF was mainly involved in Strike, Close Air Support, Aerial reconnaissance, Bomber Escort and Pathfinding missions for RAF and USAAF Heavy bombers. RAF Pilots were embedded in IAF units and vice versa to gain combat experience. IAF pilots participated in air operations in Europe as part of the RAF.During the war, the IAF went through a phase of steady expansion.
Douglas DC-3 was also added to the fleet of The Indian Airforce
New aircraft, including the US built Vultee Vengeance, Douglas DC-3 and the British Hawker Hurricane, Supermarine Spitfire and Westland Lysander, were added to its fleet. In recognition of the services rendered by the IAF, King George VI conferred the prefix "Royal" in 1945. Thereafter the IAF was referred to as the Royal Indian Air Force. In 1950, when India became a republic, the prefix was dropped and it reverted to being the Indian Air Force
After it became independent from the British Empire in 1947, British India was partitioned into the new states of the Dominion of India and the Dominion of Pakistan. Along the lines of the geographical partition, the assets of the air force were divided between the new countries. India's air force retained the name of the Royal Indian Air Force, but three of the ten operational squadrons and facilities, located within the borders of Pakistan, were transferred to the Royal Pakistan Air Force. The RIAF Roundel was changed to an interim 'Chakra' roundel derived from the Ashoka Chakra.
Around the same time, conflict broke out between them over the control of the princely state of Jammu & Kashmir. With Pakistani forces moving into the state, its Maharaja decided to accede to India in order to receive military help.The day after, the Instrument of Accession was signed, the RIAF was called upon to transport troops into the war zone.

The refugees ready to be airlifted by IAF Dakota
And this was when a good management of logistics came into help.This led to the eruption of full-scale war between India and Pakistan, though there was no formal declaration of war. During the war, the RIAF did not engage the Pakistan Air Force in air-to-air combat; however, it did provide effective transport and close air support to the Indian troops.When India became a republic in 1950, the prefix 'Royal' was dropped from the Indian Air Force. At the same time, the current IAF roundel was adopted.
By late 1971, the intensification of the independence movement in erstwhile East Pakistan lead to the Bangladesh Liberation War between India and Pakistan. On 22 November 1971, 10 days before the start of a full-scale war, four PAF F-86 Sabre jets attacked Indian and Mukti Bahini positions at Garibpur, near the international border. Two of the four PAF Sabres were shot down and one damaged by the IAF's Folland Gnats. On 3 December, India formally declared war against Pakistan following massive preemptive strikes by the PAF against Indian Air Force installations in Srinagar, Ambala, Sirsa, Halwara and Jodhpur. However, the IAF did not suffer significantly because the leadership had anticipated such a move and precautions were taken.The Indian Air Force was quick to respond to Pakistani air strikes, following which the PAF carried out mostly defensive sorties.
Within the first two weeks, the IAF had carried out almost 12,000 sorties over East Pakistan and also provided close air support to the advancing Indian Army. IAF also assisted the Indian Navy in its operations against the Pakistani Navy and Maritime Security Agency in the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea. On the western front, the IAF destroyed more than 20 Pakistani tanks,4 APCs and a supply train during the Battle of Longewala..The IAF undertook strategic bombing of West Pakistan by carrying out raids on oil installations in Karachi, the Mangla Dam and a gas plant in Sindh. Similar strategy was also deployed in East Pakistan and as the IAF achieved complete air superiority on the eastern front, the ordnance factories, runways, and other vital areas of East Pakistan were severely damaged.
IAF Hawk Hunter Fighter Jet which was involved in the Battle of Longewala
By the time Pakistani forces surrendered, the IAF destroyed 94 PAF Aircraft.The IAF was able to conduct a wide range of missions – troop support; air combat; deep penetration strikes; para-dropping behind enemy lines; feints to draw enemy fighters away from the actual target; bombing; and reconnaissance. In contrast, the Pakistan Air Force, which was solely focused on air combat, was blown out of the subcontinent’s skies within the first week of the war. Those PAF aircraft that survived took refuge at Iranian air bases or in concrete bunkers, refusing to offer a fight. Hostilities officially ended at 14:30 GMT on 17 December, after the fall of Dacca on 15 December. India claimed large gains of territory in West Pakistan (although pre-war boundaries were recognised after the war), and the independence of Pakistan's East wing as Bangladesh was confirmed.
IAF Jets bombarding in warzone against Pakistan
The IAF had flown over 16,000 sorties on both East and West fronts; including sorties by transport aircraft and helicopters. while the PAF flew about 30 and 2,840. More than 80 percent of the IAF's sorties were close-support and interdiction, and according to neutral assessments about 45 IAF Aircraft were lost while, Pakistan lost 75 aircraft. Not including any F-6s, Mirage IIIs, or the six Jordanian F-104s which failed to return to their donors. But the imbalance in air losses was explained by the IAF's considerably higher sortie rate, and its emphasis on ground-attack missions.
On the ground Pakistan suffered most, with 9,000 killed and 25,000 wounded while India lost 3,000 dead and 12,000 wounded. The loss of armoured vehicles was similarly imbalanced. This represented a major defeat for Pakistan.Towards the end of the war, IAF's transport planes dropped leaflets over Dhaka urging the Pakistani forces to surrender, demoralising Pakistani troops in East Pakistan.
Besides this, The Indian Airforce also supplied food items and other significant items during natural crisis.
IAF AN-32 was used to drop humanatarian supplies
On 11 May 1999, the Indian Air Force was called in to provide close air support to the Indian Army at the height of the ongoing Kargil conflict with the use of helicopters.The IAF strike was code named Operation Safed Sagar. The first strikes were launched on 26 May, when the Indian Air Force struck infiltrator positions with fighter aircraft and helicopter gunships.The initial strikes saw MiG-27s carrying out offensive sorties, with MiG-21s and later MiG-29s providing fighter cover.The IAF also deployed its radars and the MiG-29 fighters in vast numbers to keep check on Pakistani military movements across the border. Srinagar Airport was at this time closed to civilian air-traffic and dedicated to the Indian Air Force.
On 27 May, the Indian Air Force suffered its first fatality when it lost a MiG-21 and a MiG-27 in quick succession. The following day, while on an offensive sortie, a Mi-17 was shot down by three Stinger missiles and lost its entire crew of four.Following these losses the IAF immediately withdrew helicopters from offensive roles as a measure against the threat of Man-portable air-defence systems (MANPAD).
An IAF MIG-21
On 30 May, the Mirage 2000s were introduced in offensive capability, as they were deemed better in performance under the high-altitude conditions of the conflict zone. Mirage 2000s were not only better equipped to counter the MANPAD threat compared to the MiGs, but also gave IAF the ability to carry out aerial raids at night. The MiG-29s were used extensively to provide fighter escort to the Mirage 2000.Radar transmissions of Pakistani F-16s were picked up repeatedly, but these aircraft stayed away. The Mirages successfully targeted enemy camps and logistic bases in Kargil and severely disrupted their supply lines. Mirage 2000s were used for strikes on Muntho Dhalo and the heavily defended Tiger Hill and paved the way for their early recapture. At the height of the conflict, the IAF was conducting over forty sorties daily over the Kargil region. By 26 July, the Indian forces had successfully repulsed the Pakistani forces from Kargil.
Ranks-
Indian Air Force Ranks
Fleet-
Aircrafts and Helicopters-
Aircrafts and Helicopters-

Sukhoi Su-30 MKI
Tejas (Built by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited)
Ilyushin IL-78 MKI of IAF

Mirage 2000

MIG-29

Embrarer ERJ-145
Jaguar
C-130 Super Hercules
Antonov An-32

IAF Boeing 737-200

IAF Boeing C-17 Globemaster
Dorneir Do-288

Air India One

Air India One

Hawker Siddley HS 748

HAL HP-32 Deepak

HAL HJT-36 Sitara

HAL HJT-16 Kiran
Pipistrel Virus SW 80
BAE Hawk MK-32

HAL Dhruv
HAL Chetak

IAF Sarang
HAL Cheetah

MIL MI-8
MIL MI-17
MIL MI-26
IAI Searcher II
+Armed+Assault++Attack+Helicopter+(3).jpg)
MIL MI-35
IAI Heron

IAI Harop

DRDO Lakshya (Pilotless Trained Aircraft)
Missiles-

TRISHUL
SPYDER Missile System
S-125 Pechora

Akash Missile
9K33 OSA
Prithvi-II
Prithvi-I

No comments:
Post a Comment